Digital circuits are fundamental building blocks of modern electronics, enabling the processing and manipulation of binary data. Two essential types of digital circuits are combinational and sequential circuits. These circuits form the backbone of digital systems and are vital in various applications, from simple logic gates to complex computer processors.
In this article, we will delve into the differences between combinational and sequential circuits. While both types of circuits operate on binary inputs and outputs, they have distinct characteristics and functionalities. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers, hobbyists, and anyone interested in digital electronics to design and implement efficient and reliable circuits for their specific requirements.
Table of Contents
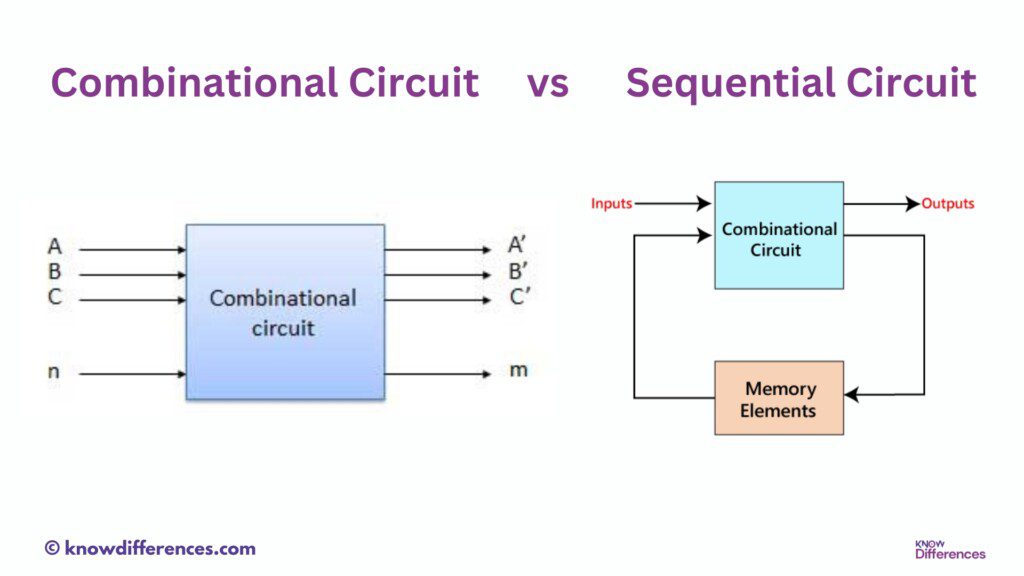
The main difference between combinational and sequential circuits is that combinational circuits have no memory elements and their output depends only on the current input values, while sequential circuits have memory elements and their output is determined by both the current input and the previous state of the circuit. Sequential circuits utilize feedback to store information temporarily, allowing them to perform tasks that involve memory and timing considerations. In contrast, combinational circuits focus on boolean operations and logic functions without the need for stored information.
The table below provides a general overview of the differences between combinational and sequential circuits:
| Differences | Combinational Circuits | Sequential Circuits |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital circuits with no memory elements | Digital circuits with memory elements |
| Output | Output depends only on current input values | Output depends on current input and previous state |
| Feedback | No feedback path from output to input | Contains feedback path, creating a loop |
| Timing | No concept of time delay or clock signal | Relies on clock signals for synchronization |
| State | Stateless, as there is no stored information | Possesses state, storing information temporarily |
| Components | Consists of logic gates and combinational elements | Involves flip-flops, registers, and memory units |
| Functionality | Performs boolean operations and logic functions | Performs both combinational and sequential tasks |
| Design Complexity | Generally simpler to design and analyze | Typically more complex to design and troubleshoot |
| Application | Used in data processing, arithmetic operations, etc. | Applied in memory units, CPUs, and control units |
| Memory Requirement | Requires less memory | Requires additional memory for storing state |
| Examples | Adders, decoders, multiplexers | Counters, shift registers, finite state machines |
What is a Combinational Circuit?
A combinational circuit is a digital circuit where the output at any given time solely depends on the present input. It does not employ memory elements or feedback loops in its design. Instead, combinational circuits use logic gates to process input signals and generate output signals directly based on the input combination.
Characteristics of Combinational Circuits
Combinational circuits possess several key characteristics:
- Stateless: Combinational circuits do not store any information about past inputs, and their output depends only on the current input.
- No Feedback: These circuits lack feedback loops, ensuring that the output is not fed back to the input.
- Instantaneous Operation: The output of a combinational circuit responds immediately to changes in input, as there are no memory elements to introduce delays.
Examples of Combinational Circuits
Combinational circuits find applications in various digital devices and systems. Some common examples include:
- Adders and Subtractors: These circuits perform binary addition and subtraction operations, crucial for arithmetic computations.
- Multiplexers and Demultiplexers: Multiplexers select one data input from multiple sources and route it to the output, while demultiplexers perform the reverse operation.
- Encoders and Decoders: Encoders convert multiple input signals into a coded output, while decoders decode the coded input into multiple output signals.
What is a Sequential Circuit?
A sequential circuit is a digital circuit that utilizes memory elements, such as flip-flops or latches, to store information. Unlike combinational circuits, the output of a sequential circuit depends not only on the present input but also on the current state of the memory elements.
Characteristics of Sequential Circuits
Sequential circuits have several key characteristics:
- Stateful: These circuits maintain a state, which represents the stored information from past inputs.
- Feedback Loops: Sequential circuits incorporate feedback loops, allowing the output to influence the state and, consequently, affect future outputs.
- Clock Dependency: They require a clock signal to synchronize the operation and ensure stable transitions of the memory elements.
Examples of Sequential Circuits
Sequential circuits are extensively used in various applications. Some common examples include:
- Flip-Flops: Flip-flops are basic building blocks of sequential circuits, capable of storing a single bit of information.
- Counters: These circuits count binary or decimal numbers and are widely used in digital clocks, frequency dividers, and sequential control systems.
- Shift Registers: Shift registers can store and shift data, making them valuable in data storage and serial data transmission applications.
Key Differences between Combinational and Sequential Circuits
Basis of Operation
The fundamental difference between combinational and sequential circuits lies in their basis of operation. Combinational circuits generate outputs solely based on the current input values, whereas sequential circuits depend on both the current inputs and the internal state of the memory elements.
Feedback Loop
Combinational circuits lack feedback loops, meaning that the output is not connected back to the input. In contrast, sequential circuits utilize feedback loops to incorporate the output back into the circuit’s state.
Clock Signal
Combinational circuits do not require clock signals, as they do not store any information. However, sequential circuits necessitate a clock signal for synchronizing their operations and ensuring stable state transitions.
Memory Element
Combinational circuits do not have memory elements, while sequential circuits include memory elements like flip-flops or latches to store data.
Design Complexity
Combinational circuits are generally simpler to design since they only involve logic gates without any state management. On the other hand, sequential circuits tend to be more complex due to the incorporation of memory elements and feedback loops.
Advantages and Applications of Combinational Circuits
Combinational circuits offer several advantages in digital system design:
- Simplicity: Their straightforward nature makes them easier to implement and troubleshoot.
- Speed: Combinational circuits respond immediately to changes in inputs, leading to high-speed operation.
- Arithmetic Operations: These circuits are indispensable in arithmetic computations, such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication.
Combinational circuits find applications in numerous areas:
- Arithmetic and Logic Units (ALUs): ALUs in CPUs heavily utilize combinational circuits for arithmetic calculations.
- Data Encoding: In data communication, encoding schemes often involve combinational circuits.
- Data Multiplexing: Combinational circuits are used for data selection and multiplexing in various systems.
Advantages and Applications of Sequential Circuits
Sequential circuits bring forth unique advantages:
- Memory: The ability to store past inputs allows sequential circuits to process data with history, suitable for various control systems.
- Time-based Operations: Sequential circuits are well-suited for applications where actions must occur in a specific order or at precise intervals.
- State Machines: Sequential circuits form the foundation for designing state machines, used in complex control systems and protocols.
Sequential circuits find applications in diverse fields:
- Counters and Timers: Sequential circuits play a critical role in counters used for counting events and timers for time-based operations.
- Memory Units: Memory modules in computers and other digital devices use sequential circuits for data storage and retrieval.
- Digital Communication: Sequential circuits facilitate data synchronization and error correction in communication protocols.
Conclusion
In conclusion, combinational and sequential circuits are two fundamental types of digital circuits, each serving distinct purposes in electronics and digital systems. Combinational circuits operate solely based on the current input values and do not incorporate memory elements or feedback loops. In contrast, sequential circuits rely on memory elements and feedback loops, considering both the current inputs and past states to generate outputs. The choice between these circuit types depends on the specific requirements of a given application. By understanding their differences and applications, electronics engineers can make informed decisions and design efficient and reliable digital systems for various industries and technological domains.