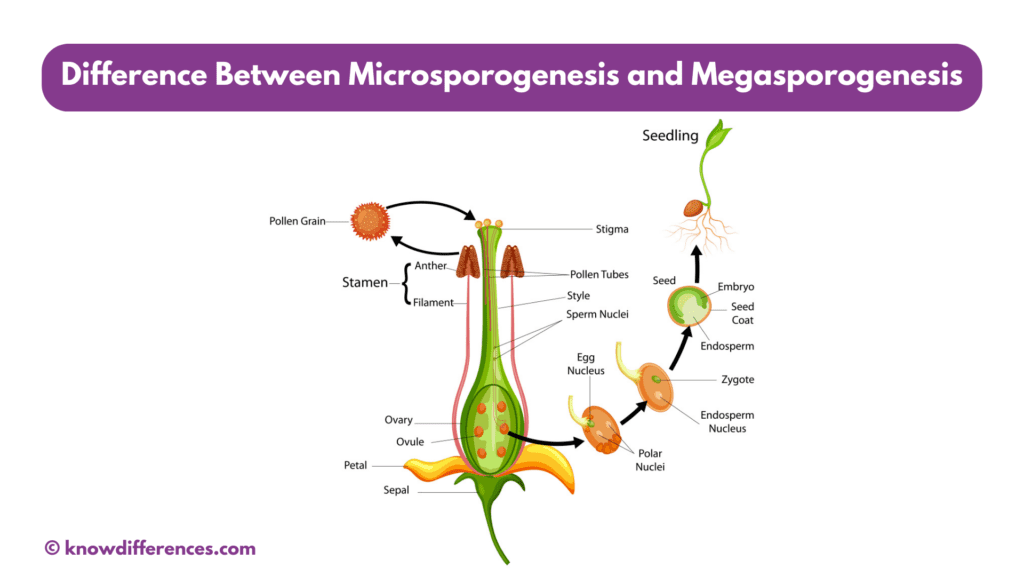
In plant biology, the processes of microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis play a crucial role in the reproduction of flowering plants. These processes are essential for the formation of male and female reproductive structures, which, in turn, facilitate the continuation of plant species. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the difference between microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis, exploring their definitions, stages, and significance in the life cycle of plants.
Table of Contents
The main difference between microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis lies in the types of spores produced and their respective roles in plant reproduction. Microsporogenesis produces microspores, which develop into male gametophytes or pollen grains, while megasporogenesis yields megaspores, leading to the formation of female gametophytes within ovules.
Here is a table highlighting key differences between Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis:
| Feature | Microsporogenesis | Megasporogenesis |
|---|---|---|
| Process Occurrence | Occurs in Microsporangia (pollen sacs) of male reproductive organs (anthers) | Takes place in the ovule within the ovary of the female reproductive organ (ovule) |
| Purpose | Formation of microspores (male gametophytes) for sexual reproduction | Formation of megaspores (female gametophytes) for sexual reproduction |
| Location | Anthers of the stamen in the flower | Ovules inside the ovary of the pistil in the flower |
| Meiotic Division | Undergoes meiosis to produce haploid microspores | Undergoes meiosis to produce haploid megaspores |
| Number of Products | Typically results in four microspores per pollen sac | Usually yields one functional megaspore per ovule |
| Size of Spores | Microspores are relatively smaller in size | Megaspores are generally larger in size |
| Fate of Spores | Microspores develop into pollen grains (male gametophytes) | Megaspores develop into the female gametophyte |
| Cellular Surroundings | Surrounded by diploid cells in the anther | Surrounded by diploid tissue layers in the ovule (integuments) |
| Timing in Plant Life Cycle | Typically occurs earlier in the plant life cycle | Generally occurs later in the plant life cycle |
| Surrounded by diploid cells in the other | Produces pollen, which is transferred to the stigma for fertilization | Produces ovules, which remain within the ovary for potential fertilization |
Plant Reproduction Basics
Before we dive into the specifics of microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis, it’s important to have a basic understanding of plant reproduction. Plants, like animals, reproduce to ensure the survival and propagation of their species. However, plant reproduction follows unique mechanisms that involve both sexual and asexual processes.
Plant Reproductive Structures
Plant reproduction involves the use of specialized reproductive structures, primarily found in flowering plants (angiosperms). These structures include flowers, seeds, and cones in gymnosperms. The most important components for our discussion are the male and female reproductive organs within a flower.
In a typical flower, the male reproductive organ is the stamen, which consists of the anther and the filament. The anther produces pollen, which contains the male gametes (sperm). The female reproductive organ is the pistil, which comprises the stigma, style, and ovary. The ovary contains the female gametes (ovules).
Male and Female Gametophytes
To understand microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis, it’s crucial to grasp the concept of gametophytes. In the plant life cycle, there are two generations: the sporophyte and the gametophyte. The sporophyte is the dominant, more familiar generation – the mature plant you see in your garden. It produces spores, which are reproductive cells.
The spores give rise to the gametophyte generation, which is much smaller and less conspicuous. In the context of microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis, we focus on the male and female gametophytes.
The male gametophyte, or microgametophyte, is responsible for producing sperm cells. The process leading to their formation is microsporogenesis. On the other hand, the female gametophyte, or megagametophyte, plays a role in the development of egg cells, and this process is known as megasporogenesis.
Microsporogenesis
Definition and Purpose
Microsporogenesis is the process through which microspores, which eventually become male gametophytes, are produced in the anther of a flower. These microspores are essential for fertilization, as they contain the male gametes (sperm) required for sexual reproduction in plants.
Stages of Microsporogenesis
Microsporogenesis consists of several distinct stages, each playing a vital role in the formation of functional microspores. These stages can be summarized as follows:
Microspore Mother Cell (MMC)
The process of microsporogenesis begins with the division of a specialized cell called the microspore mother cell (MMC). This division is initiated by environmental and genetic cues.
Meiosis
Following the division of the MMC, meiosis takes place, resulting in the formation of haploid microspores. These microspores have half the chromosome number of the original MMC.
Microspore
The microspores, now haploid, are released from the tetrads, which are groups of four haploid microspores, into the anther sac. Here, they undergo further development to become functional male gametophytes.
Pollen Grains
The final stage of microsporogenesis involves the transformation of microspores into pollen grains. Each pollen grain contains a generative cell that divides to produce two sperm cells. The sperm cells are the male gametes needed for fertilization.
Significance of Microsporogenesis
Microsporogenesis is a fundamental process in plant reproduction. It leads to the production of pollen grains, which are essential for pollination and fertilization. When pollen grains land on the stigma of a flower, they germinate and release their sperm cells, which fertilize the egg cells in the ovule. This fertilization process results in the formation of seeds and, ultimately, new plants.
Megasporogenesis
Definition and Purpose
Megasporogenesis is the counterpart to microsporogenesis. While microsporogenesis leads to the formation of male gametophytes, megasporogenesis is the process by which megaspores are produced in the ovule of a flower. These megaspores give rise to the female gametophyte, which is essential for the development of egg cells and sexual reproduction in plants.
Stages of Megasporogenesis
Megasporogenesis, like microsporogenesis, involves several distinct stages that culminate in the production of functional megaspores. These stages can be summarized as follows:
Megaspore Mother Cell (MMC)
The process of megasporogenesis begins with a specialized cell known as the megaspore mother cell (MMC). This cell undergoes a series of divisions that result in the formation of megaspores.
Meiosis
Meiosis in megasporogenesis is a bit different from that in microsporogenesis. In this case, only one of the four haploid cells produced by meiosis becomes a functional megaspore, while the others degenerate.
Functional Megaspore
The single functional megaspore, which has a haploid chromosome number, remains intact and undergoes further development within the ovule.
Female Gametophyte
The functional megaspore develops into the female gametophyte, often referred to as the embryo sac. This structure houses the egg cell, which is essential for fertilization.
Significance of Megasporogenesis
Megasporogenesis is crucial for plant reproduction, as it results in the formation of the female gametophyte and, ultimately, the egg cell. The egg cell plays a central role in the fertilization process, as it must be fertilized by a sperm cell from the pollen grain to produce seeds. These seeds are the next generation of plants, ensuring the continuation of the plant species.
Key Differences
Now that we have explored the processes of microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis in detail, let’s highlight the key differences between these two essential processes in plant reproduction.
Location
One of the primary differences between microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis is their location within the flower.
- Microsporogenesis: This process occurs within the anther, which is part of the stamen, the male reproductive organ of the flower.
- Megasporogenesis: Megasporogenesis takes place in the ovule, which is part of the pistil, the female reproductive organ of the flower.
Types of Spores Produced
Both processes result in the formation of spores, but the type of spores produced differs.
- Microsporogenesis: Microsporogenesis leads to the production of microspores, which are haploid and give rise to the male gametophyte (pollen grains) containing sperm cells.
- Megasporogenesis: Megasporogenesis produces megaspores, with only one of these being functional. The functional megaspore develops into the female gametophyte, which houses the egg cell.
Gametophyte Development
Microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis are associated with the development of different gametophytes.
- Microsporogenesis: The male gametophyte, known as the microgametophyte, is produced. It matures within the pollen grain and contains two sperm cells.
- Megasporogenesis: The female gametophyte, referred to as the megagametophyte or embryo sac, is formed. It includes the egg cell, which is essential for fertilization.
Timing of Events
The timing of microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis in the plant’s life cycle is distinct.
- Microsporogenesis: Microsporogenesis occurs earlier in the life cycle, typically before the flower is fully developed, as pollen must be available when the flower blooms to facilitate pollination.
- Megasporogenesis: Megasporogenesis takes place within the ovule, often after the flower has fully developed. It is in the ovule that the female gametophyte is formed and fertilization occurs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis represent essential processes in the reproductive cycle of flowering plants, each contributing to the formation of male and female gametophytes, respectively. While microsporogenesis leads to the production of pollen grains for the transfer of male gametes, megasporogenesis results in the formation of ovules for the reception and fertilization of female gametes. Understanding the distinctions between these processes is fundamental to comprehending the intricate mechanisms underlying plant reproduction and ensuring the continuity of plant